Pseudomonas Management
What is Pseudomonas?
Pseudomonas is an opportunistic pathogen (P.aeruginosa) which is typically referred to as Pseudomonas. It is a microorganism (bacteria) that can cause infections, especially within individuals with weakened immune systems. These infections can include urinary tract, respiratory, soft tissue, bone and tissue, gastrointestinal and a variety of other systemic infections.
Healthy individuals may also be susceptible (especially after exposure to water which contains Pseudomonas) with infections typically being milder and can include symptoms such as ear infections, skin rashes, abscess formation and other infections.
Where is Pseudomonas Found?
Pseudomonas is found naturally in the environment, mainly in soil and water, but can also be found on plants, animals and humans. Pseudomonas is considered to be a robust bacteria and has the ability to survive under a variety of environmental conditions.
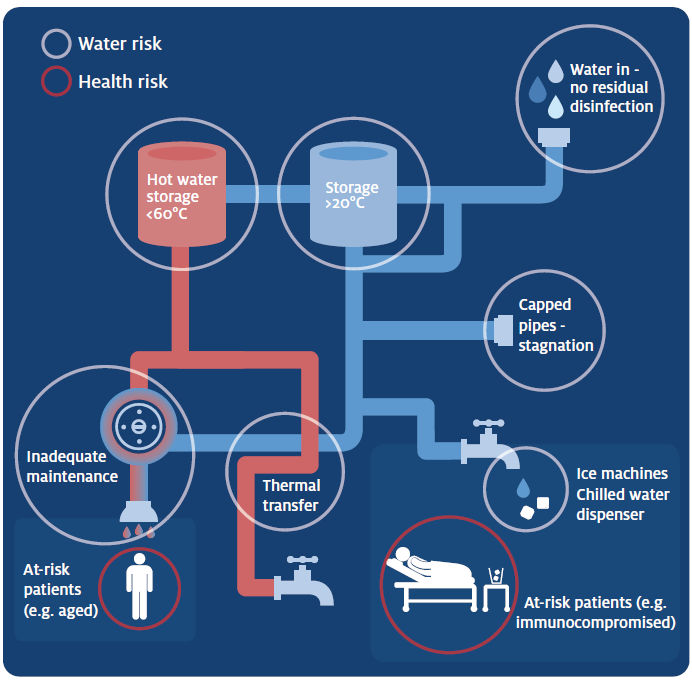
Pseudomonas is known to proliferate in moist or wet areas and can survive for extended periods of time on a number of surfaces typically found within commercial and health and aged care facilities such as ice machines, taps, shower heads, basins, spa baths, swimming pools, pipework (up to 2 meters) and other surfaces. In its planktonic form is a dynamic, fast-swimming bacterium, however, it can also occur within biofilm attached to some surfaces or substrates.
Pseudomonas is likely to occur in areas where water is stagnant, there is low disinfectant residual, the water temperature is suitable, where outlets are not adequately cleaned or when basins or sinks are used incorrectly.
Pseudomonas is known to proliferate at temperatures ranging between 25–42°C with the optimum temperature being 37°C.
How do you Effectively Manage Pseudomonas?
The effective Pseudomonas management requires a holistic approach which includes at site specific risk assessment and implementation of the associated control measures. These may include:
- Temperature controls
- Maintenance of adequate residual disinfection
- Formalised flushing programs
- Physical cleaning and disinfection of surfaces / equipment
- Maintenance of adequate cleanliness
- Correct design and use of water systems and associated equipment
- Correct use and layout of hand basins / sinks (e.g. designed to reduce risk of ‘splash back’)
- Other applicable controls.
The effective and holistic management of opportunistic pathogens such as Pseudomonas is central to health and aged care facilities and should hence not be overlooked.
For more information, advice or if you suspect your facility may be at risk please feel free to contact us for more information.
